🎙️ AI Agents - Podcast Creator with Fully Local Setup
We increasingly hear about AI Agents — i usually say that we have entered what is being called the “Agentic Spring”, a phase where trends are shifting towards developing autonomous, specialized AI rather than all-knowing generalist assistants.
For this reason, I decided to explore the emerging frameworks that are rapidly gaining traction, testing their potential, understanding how they work and what these agentic frameworks can achieve.
I wanted to test their capabilities on a non-trivial use case. So, I decided to implement a podcast generation system that extracts content from a website and transforms it into a structured audio narrative. I took inspiration from Google’s Notebook LM, simulating a similar workflow where AI agents analyze and structure content before converting it into a narrated podcast.
For this project in particular i implemented a fully local agentic podcast creation pipeline utilizing:
- Ollama to run local LLMs.
- CrewAI framework for the AI Agent orchestration.
- Coqui TTS for audio generation.
- Streamlit for creating an interactive web UI.
The application automates the entire workflow of transforming news content from a website into a structured podcast with narration. Additionally, this project highlights how to enable interaction between two distinct crews within CrewAI, making it a versatile example for adapting to other use cases involving multiple collaborating crews.
🛠️ How It Works
Below i reported the overall schema of the Agentic Crews and Agents: 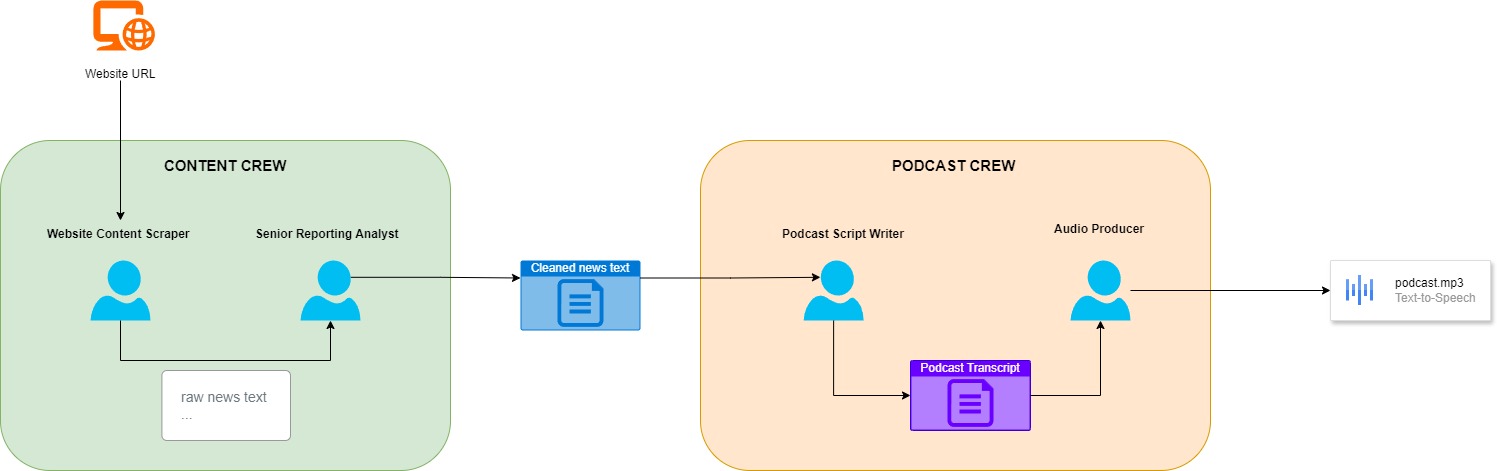
Step 1: Provide a News URL
The user inputs a news URL. This URL becomes the starting point for scraping and processing content.
Step 2: News Processing Crew
The News Processing Crew handles:
- Scraping: Extracting and cleaning the main content from the website.
- Reporting: Generating a detailed report based on the scraped content.
Step 3: Podcast Creation Crew
The Podcast Creation Crew takes the processed content and performs:
- Script Writing: Crafting a structured podcast script in Italian (or whatever language do you prefer).
- Audio Generation: Converting the script into an audio file (MP3) using Coqui TTS.
Step 4: Save Results
- The scraped content is saved locally for traceability.
- The podcast audio is saved as an MP3 file in the
podcastsdirectory.
🧩 Components and Interactions
There are 2 Crews that interact with each other: News Processing Crew and Podcast Creation Crew:
1. 👥 News Processing Crew
This crew focuses on extracting and analyzing content from the provided URL.
Agents
- Website Content Scraper:
- Role: Extract the main content of the specified website URL.
- Tools: Uses the
ScrapeWebsiteToolfor efficient web scraping. - Output: Cleaned and relevant content in Italian.
- Senior Reporting Analyst:
- Role: Analyze the scraped content and generate a detailed report.
- Skills: Expertise in turning complex data into clear, actionable reports.
Tasks
- Scrape Website Content:
- Description: Extract and clean the main content from the specified website.
- Expected Output: A full report with the main topics in Italian.
- Content Reporting:
- Description: Analyze the scraped content and expand each topic into a detailed section or provide key insights for multiple topics.
- Expected Output: A detailed report in Italian with approximately six paragraphs.
2. 👥 Podcast Creation Crew
This crew converts processed content into a podcast script and generates the final audio file.
Agents
- Podcast Script Writer:
- Role: Convert the processed content into a structured and engaging podcast script.
- Output: A natural, dialogue-based script in Italian.
- Audio Producer:
- Role: Generate high-quality MP3 audio from the podcast script.
- Tools: Uses a custom defined tool that exploits Coqui TTS for local text-to-speech synthesis.
- Output: An MP3 file of the podcast narration.
Tasks
- Script Writing:
- Description: Create a structured podcast script based on the processed content.
- Expected Output: A podcast script in Italian with a single speaker.
- Audio Generation:
- Description: Convert the podcast script into an MP3 audio file.
- Expected Output: A high-quality MP3 file (
podcasts/podcast_{timestamp}.mp3).
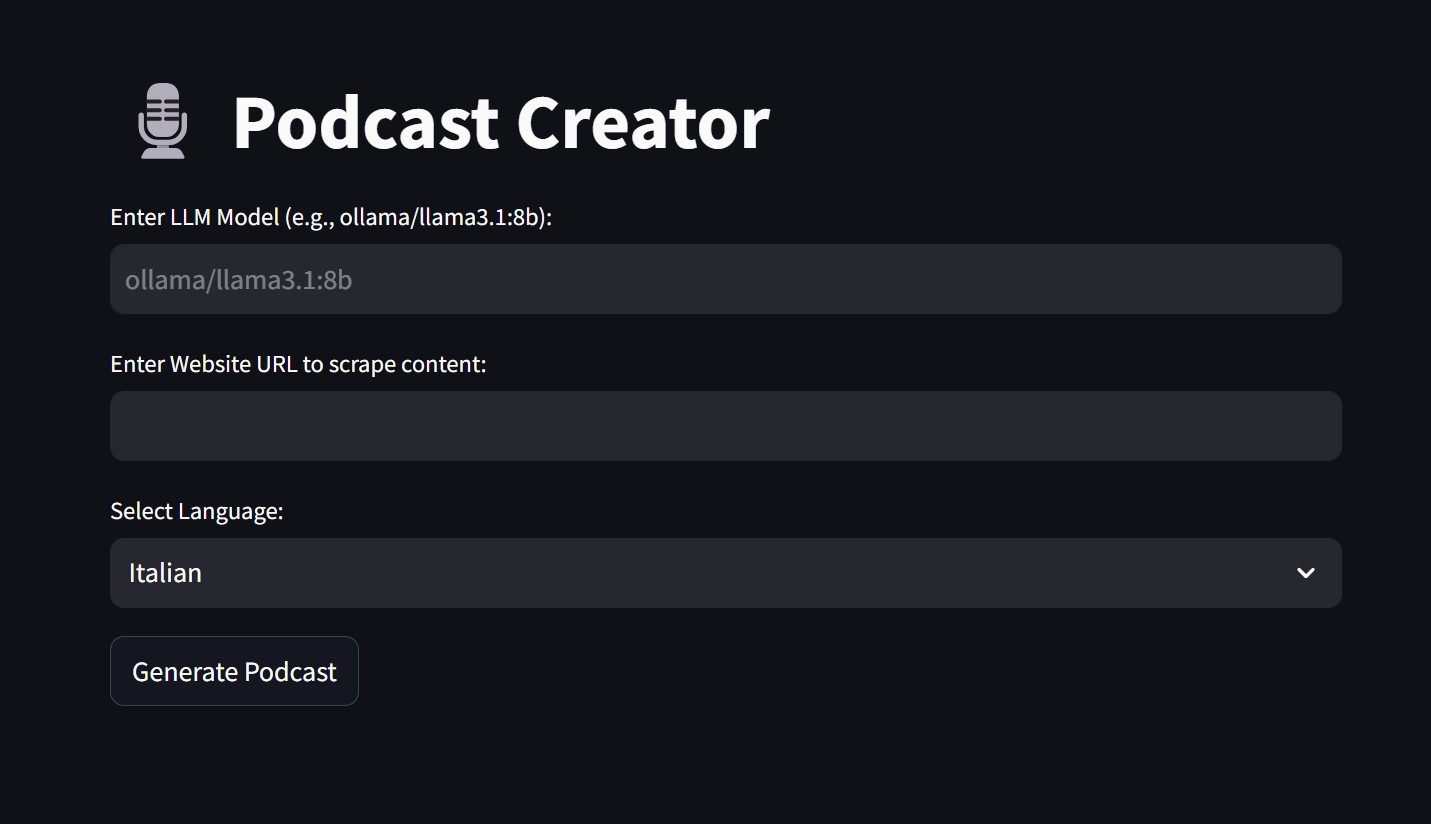
🎛️ A UI Podcast Creator
To make this project even more accessible, I also developed a UI-based version using Streamlit, allowing users to interact with the system in a more intuitive way. Instead of running commands manually, users can simply enter the required details in a web-based interface and generate a podcast effortlessly:
Key Features of the UI Version:
✅ User-friendly Interface: A web-based UI powered by Streamlit for easy interaction.
✅ Customizable Inputs: Users can specify the local LLM model, enter a news URL, and select their preferred language.
✅ Automated Workflow: The system scrapes, processes, and generates podcasts.
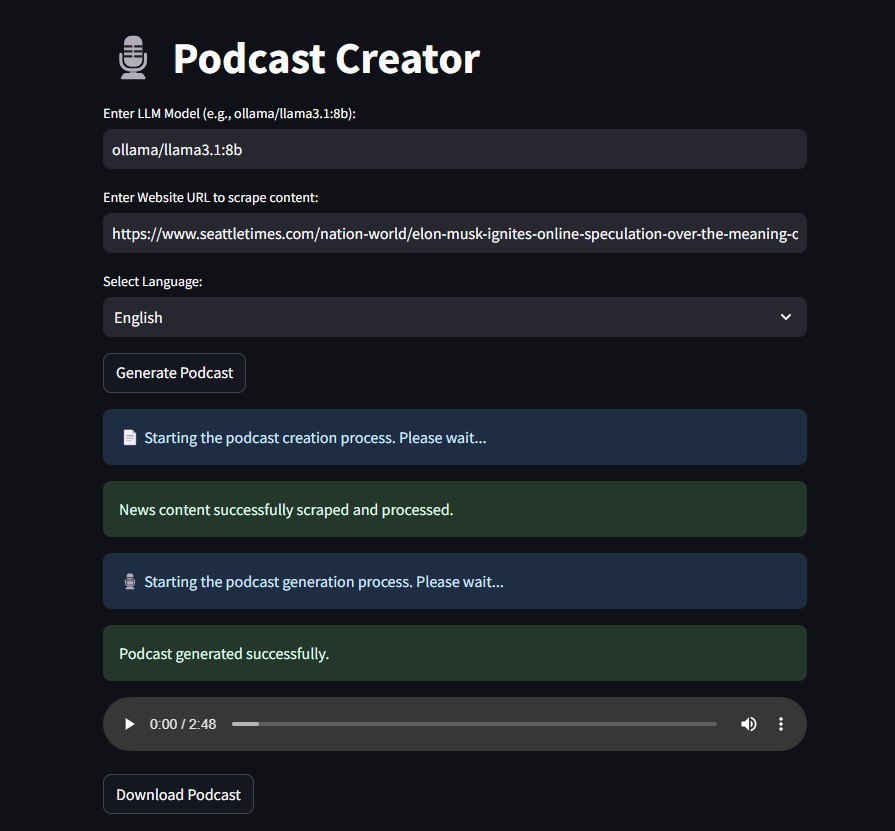
✅ Instant Audio Playback & Download: The generated podcast is available for immediate playback and download directly from the UI.
📁 Project Structure
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
.
├── src/
│ ├── podcast_creator_from_url_ollama_coquiTTS/
│ │ ├── tools/
│ │ │ └── text_to_speech_tool.py # Coqui TTS integration for audio generation
│ │ └── main.py # main script
| | └── streamlit_app.py # UI version
│ └── ...
├── output/
│ ├── scraped_news.txt # Saved content from the news scraping task
├── podcasts/
│ └── podcast.mp3 # Generated podcast audio file
├── voices/ # Contains the reference wav files for voice cloning
└── README.md # Project documentation
🚀 How to Run
Install FFmpeg:
- Download FFmpeg from the official FFmpeg website or use a package manager suitable for your operating system.
- Add FFmpeg to your system’s PATH:
- Windows: Add the
bindirectory of FFmpeg to your system’s environment variables under thePath. - Linux/MacOS: Install FFmpeg using a package manager (e.g.,
apt install ffmpegon Ubuntu orbrew install ffmpegon macOS) and ensure it’s accessible in the terminal.
- Windows: Add the
- Verify installation:
1
ffmpeg -versionIf the command outputs the version details, FFmpeg is correctly installed and configured.
- Make sure Ollama is running on your system and to have some local LLM downloaded.
- Clone the repository:
1 2
git clone https://github.com/enricollen/AIAgents cd crewAI/podcast_creator_from_url_ollama_coquiTTS - Create and activate a virtual environment to manage dependencies:
1 2 3
python -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate # On Linux/MacOS venv\Scripts\activate # On Windows
- Install required dependencies:
1
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Create a .env file in the project root path (see .env_example for reference) and configure environment variables:
1 2
LLM_MODEL=llama3.1:8b WEBSITE_URL=https://example.com/news-article
- Run the CLI version of the app:
1 2
cd src/podcast_creator_from_url_ollama_coquiTTS python main.py
or the UI version:
1 2
cd src/podcast_creator_from_url_ollama_coquiTTS python streamlit_app.py
🔗 GitHub Repository
Visit the project repository here for accessing the codebase (if you enjoyed this content, please consider leaving a star ⭐).
🎧 Podcast Demo
Below there are a couple of demos of the final podcast audio, created in English and Italian respectively:
Screenshots 📸
Here is a screenshot illustrating the UI version of the app: